🪄 Transition Rules
Description
Transition rules are OmniGibson's method for simulating complex physical phenomena not directly supported by the underlying omniverse physics engine, such as slicing, blending, and cooking. A given TransitionRule dynamically checks for its internal sets of conditions, and, if validated, executes its corresponding transition.
Transition Rules must be enabled before usage!
To enable usage of transition rules, gm.ENABLE_TRANSITION_RULES (1) must be set!
- Access global macros via
from omnigibson.macros import gm
Usage
Creating
Because TransitionRules are monolithic classes, these should be defined before OmniGibson is launched. A rule can be easily extended by subclassing the BaseTransitionRule class and implementing the necessary functions. For a simple example, please see the SlicingRule class.
Runtime
At runtime, each scene owns a TransitionRuleAPI instance, which automatically handles the stepping and processing of all defined transition rule classes. For efficiency reasons, rules are dynamically loaded and checked based on the object / system set currently active in the scene. A rule will only be checked if there is at least one valid candidate combination amongst the current object / system set. For example, if there is no sliceable object present in this scene, then SlicingRule will not be active. Every time an object / system is added / removed from the scene, all rules are refreshed so that the current active transition rule set is always accurate.
In general, you should not need to interface with the TransitionRuleAPI class at all -- if your rule implementation is correct, then the API will automatically handle the transition when the appropriate conditions are met!
Types
OmniGibson currently supports _ types of diverse transition rules, each representing a different complex physical phenomena:
SlicingRuleEncapsulates slicing an object into halves (e.g.: slicing an apple). Required Candidates
Conditions
Transition
|


|
DicingRuleEncapsulates dicing a diceable into small chunks (e.g.: dicing an apple). Required Candidates
Conditions
Transition
|
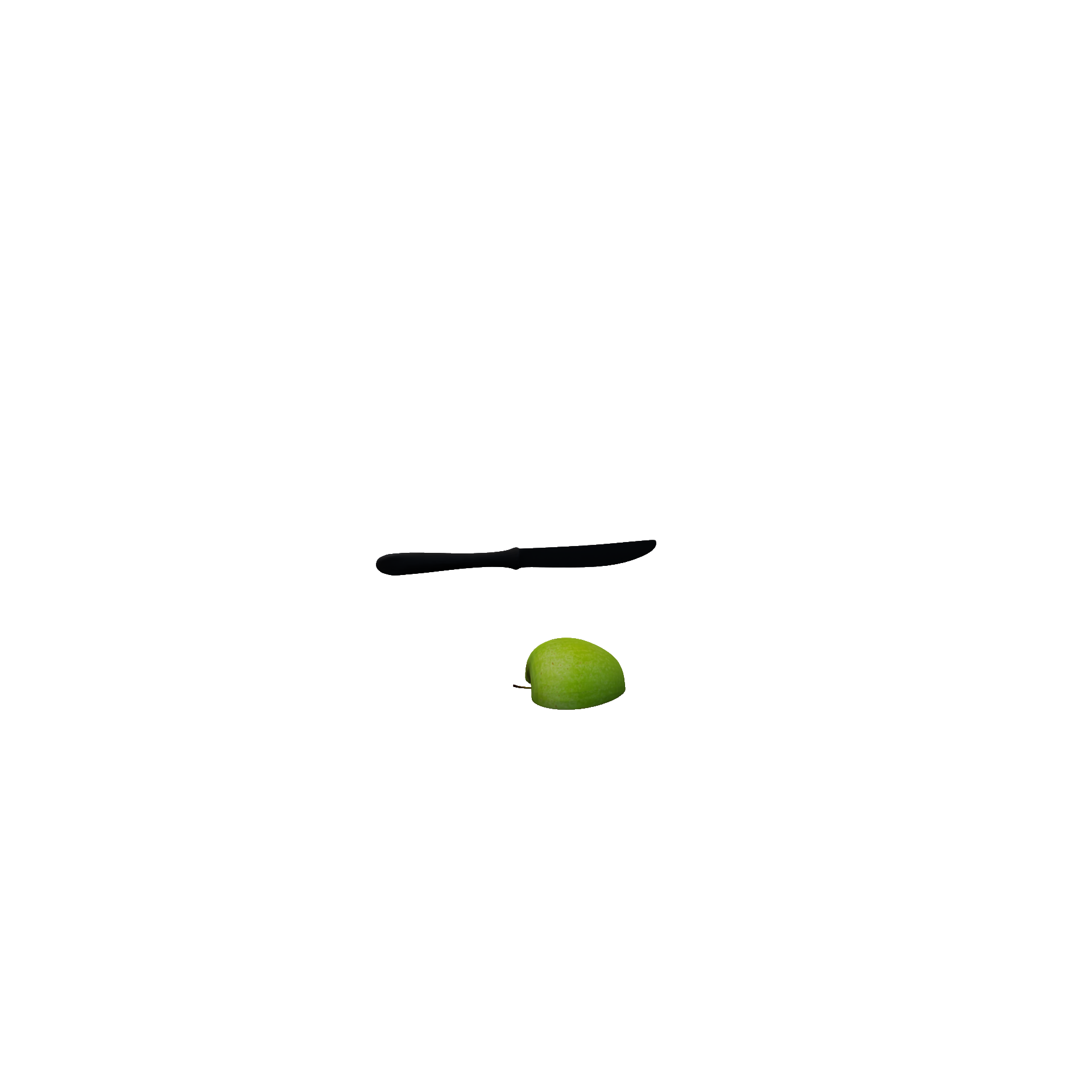


|
MeltingRuleEncapsulates melting an object into liquid (e.g.: melting chocolate). Required Candidates
Conditions
Transition
|
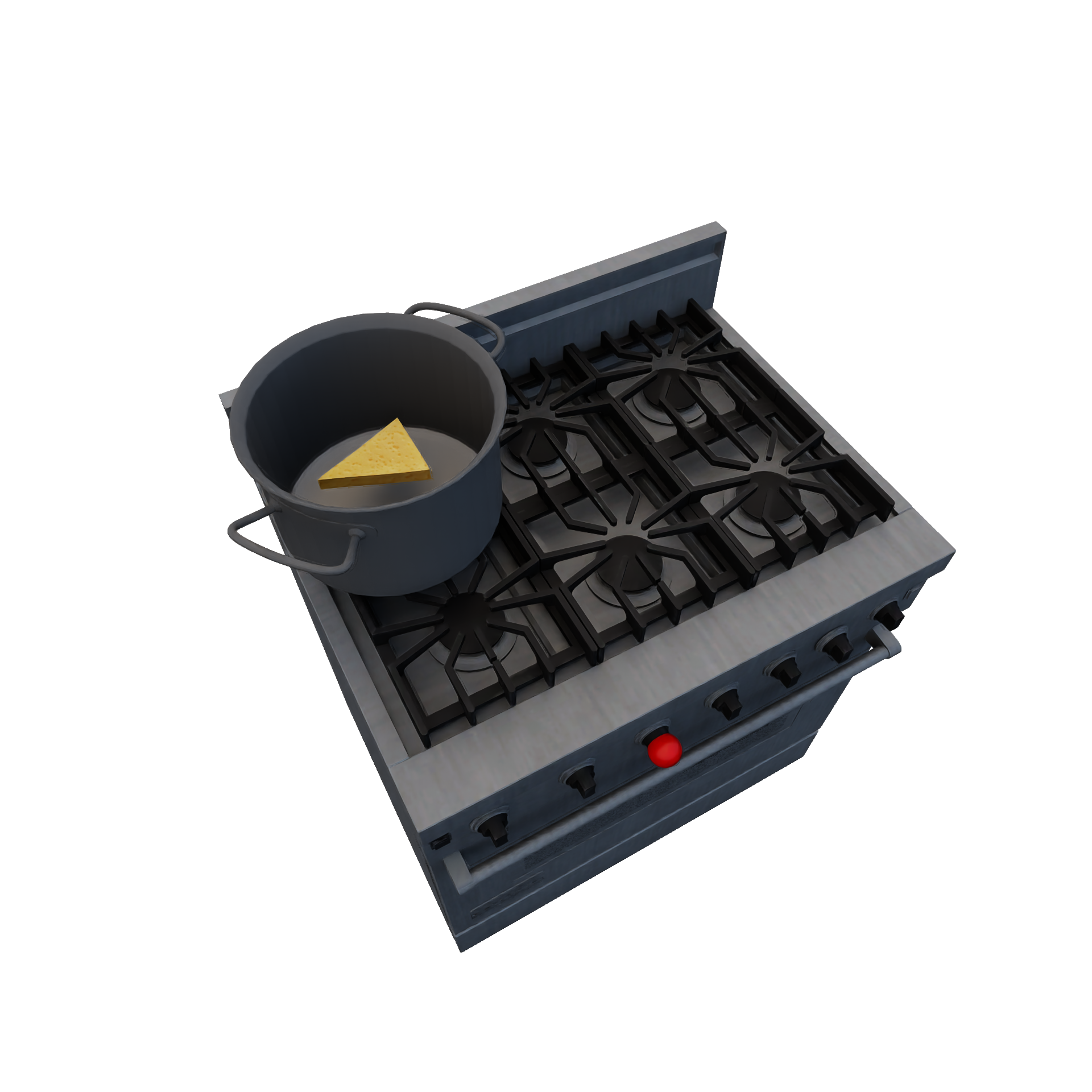
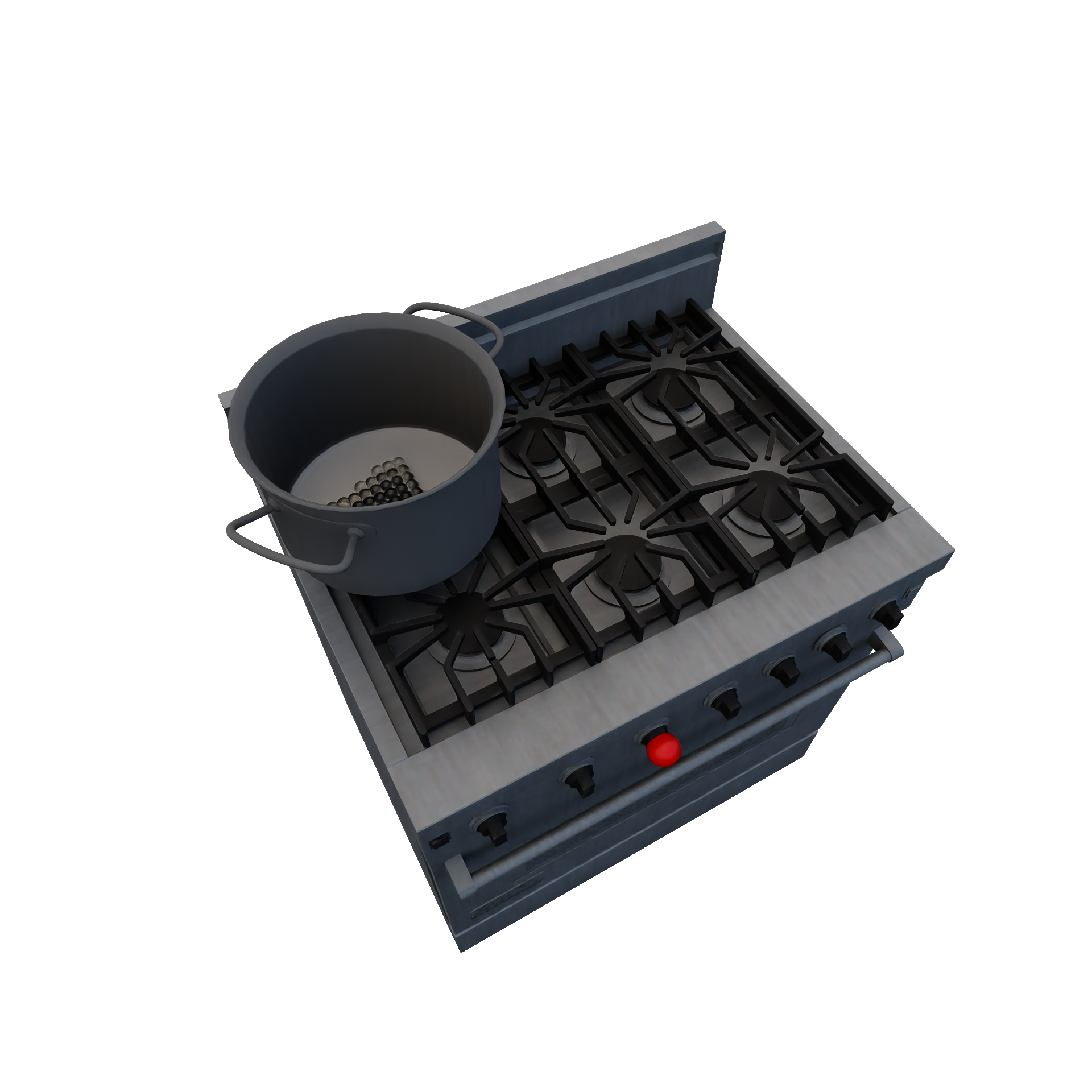


|
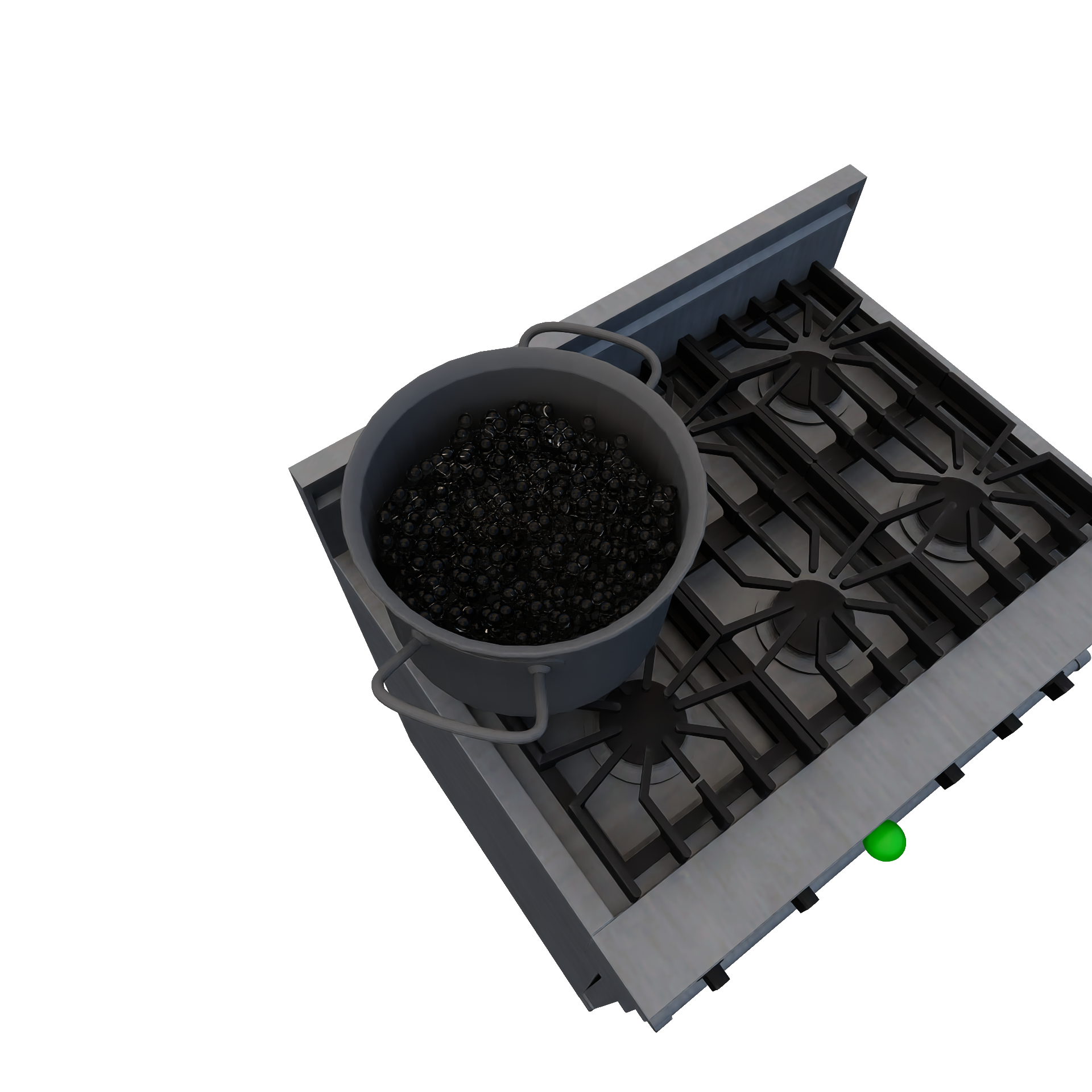
CookingPhysicalParticleRuleEncapsulates cooking physical particles (e.g.: boiling water). Required Candidates
Conditions
Transition
|
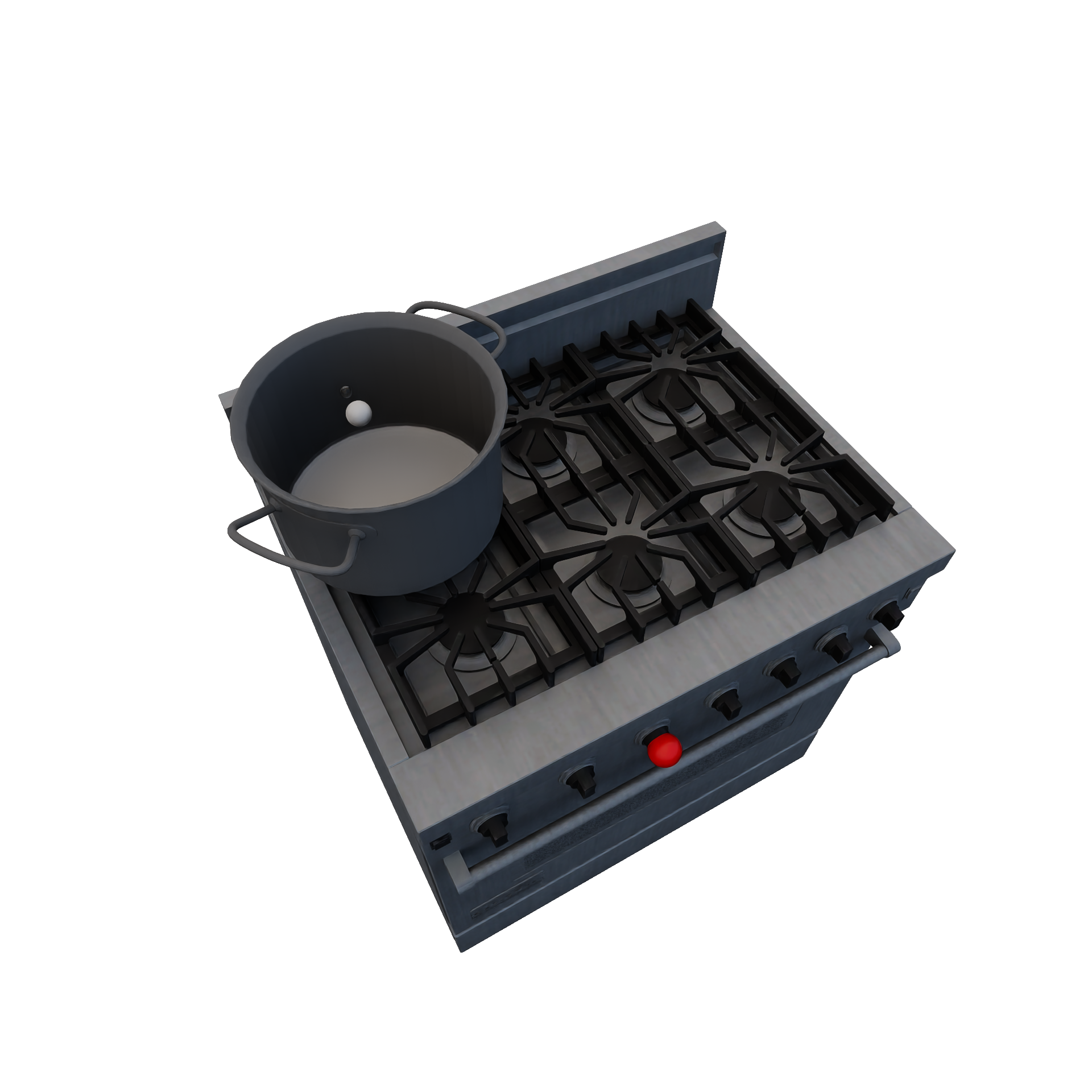
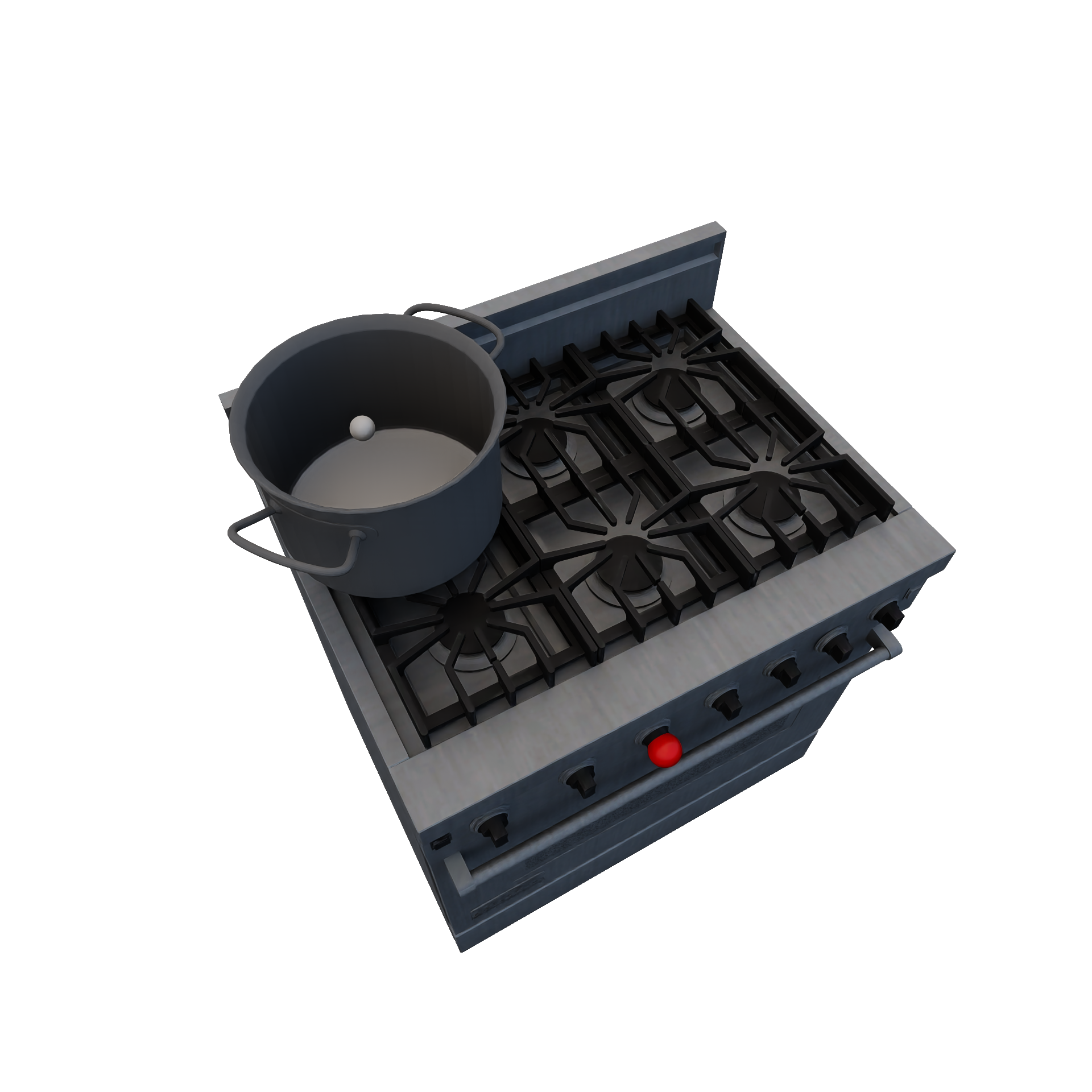


|
ToggleableMachineRuleEncapsulates transformative changes when a button is pressed (e.g.: blending a smoothie). Valid transitions are defined by a pre-defined set of "recipes" (input / output combinations). Required Candidates
Conditions
Transition
|
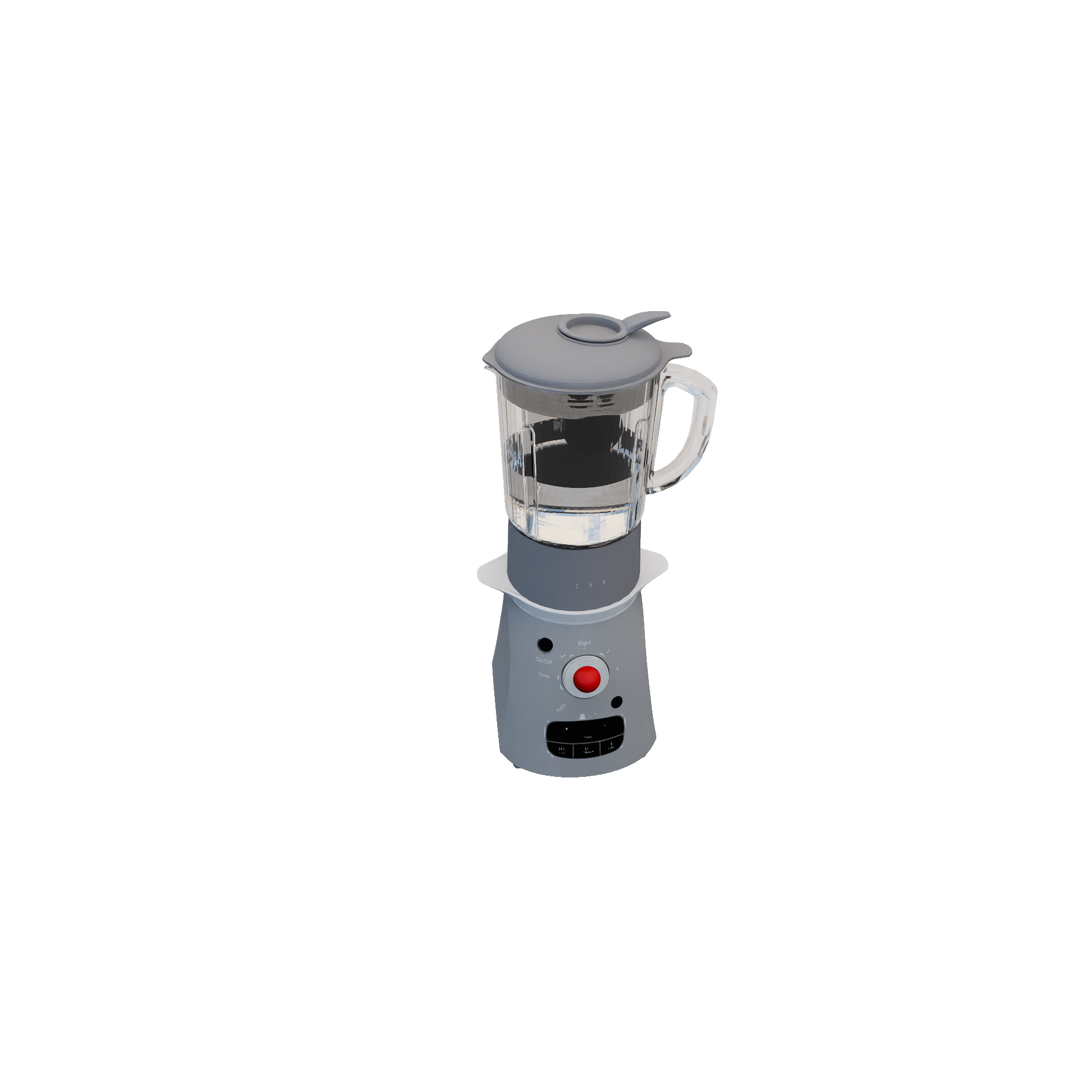
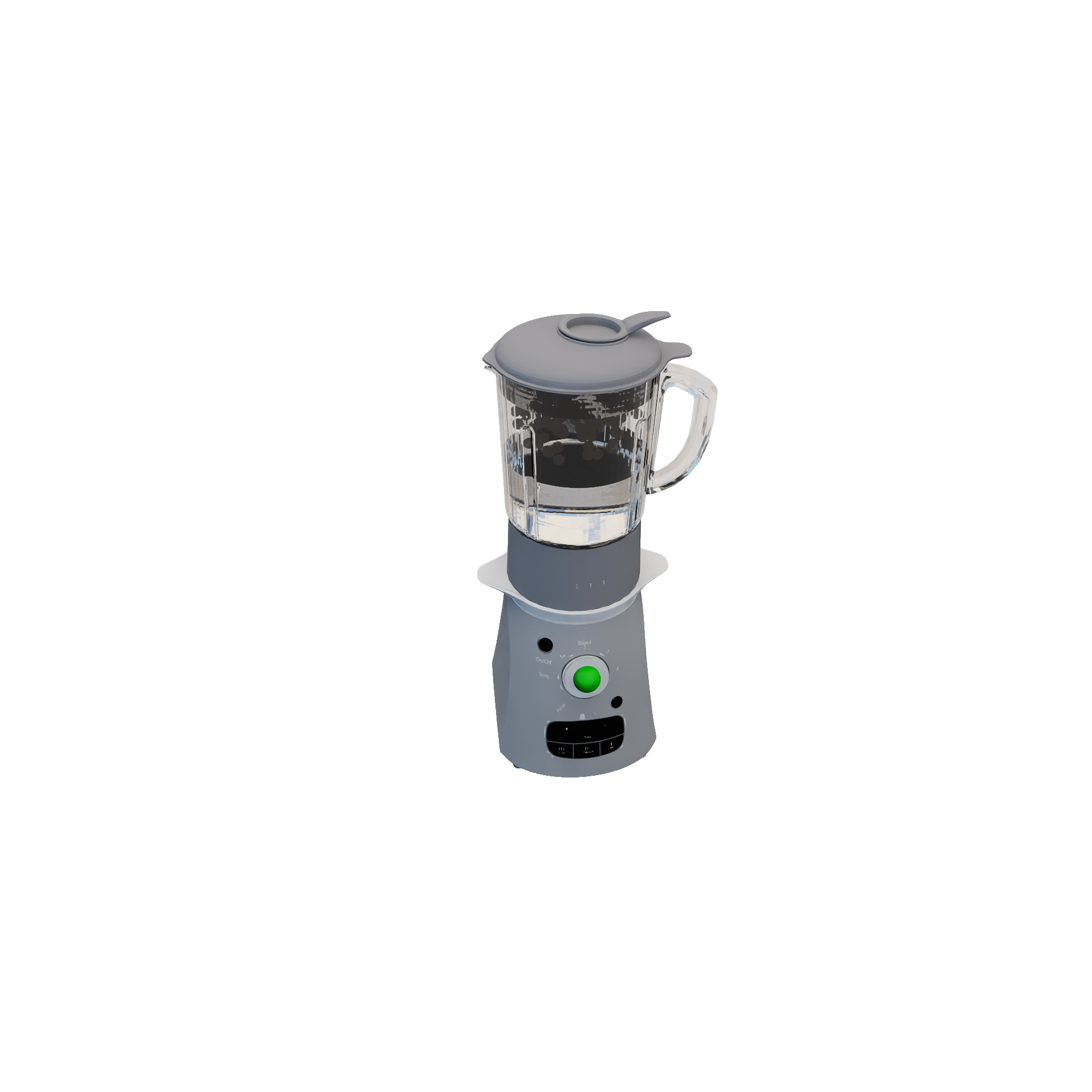


|
MixingToolRuleEncapsulates transformative changes during tool-driven mixing (e.g.: mixing a drink with a stirrer). Valid transitions are defined by a pre-defined set of "recipes" (input / output combinations). Required Candidates
Conditions
Transition
|


|
CookingRuleEncapsulates transformative changes during cooking (e.g.: baking a cake). Valid transitions are defined by a pre-defined set of "recipes" (input / output combinations). Required Candidates
Conditions
Transition
|
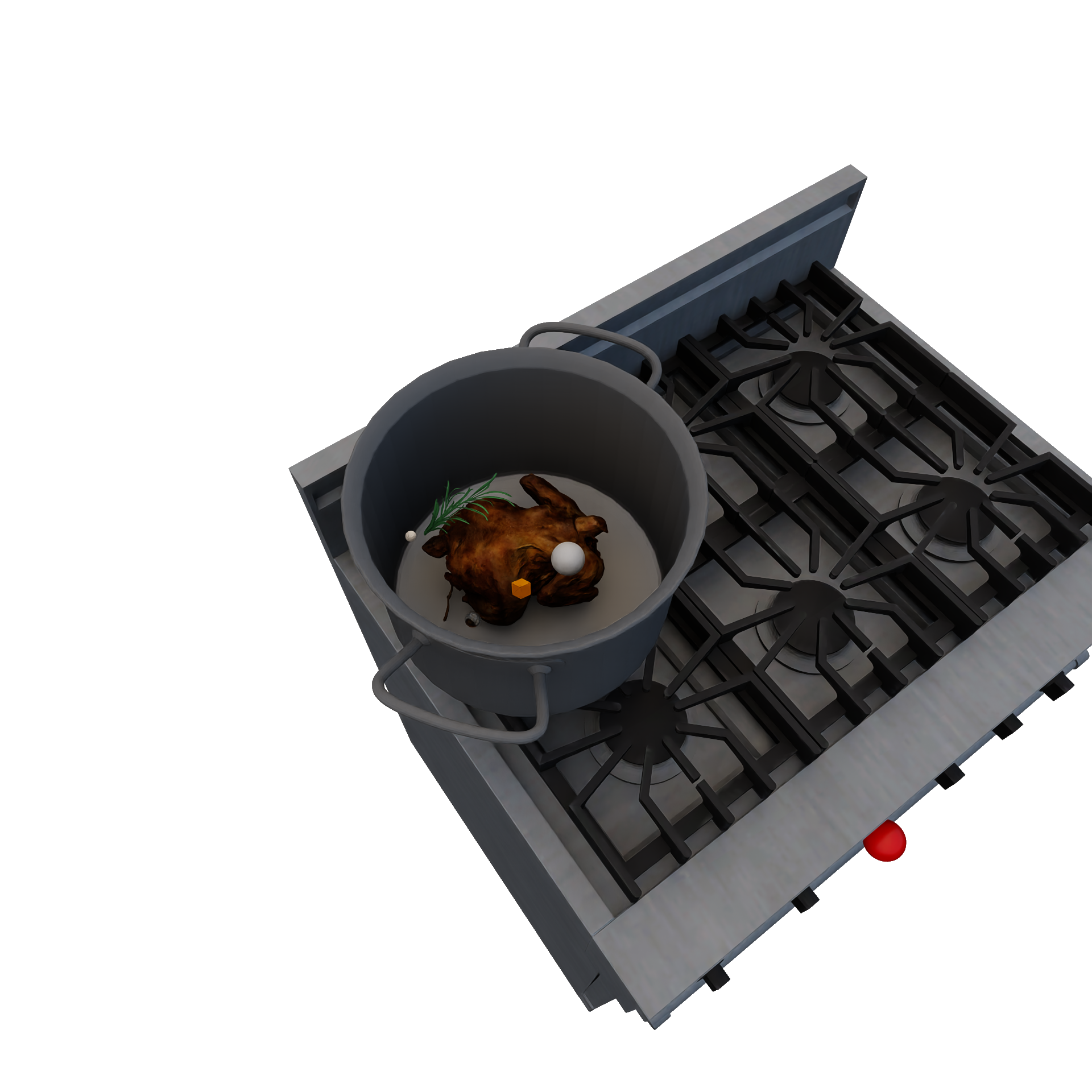

|
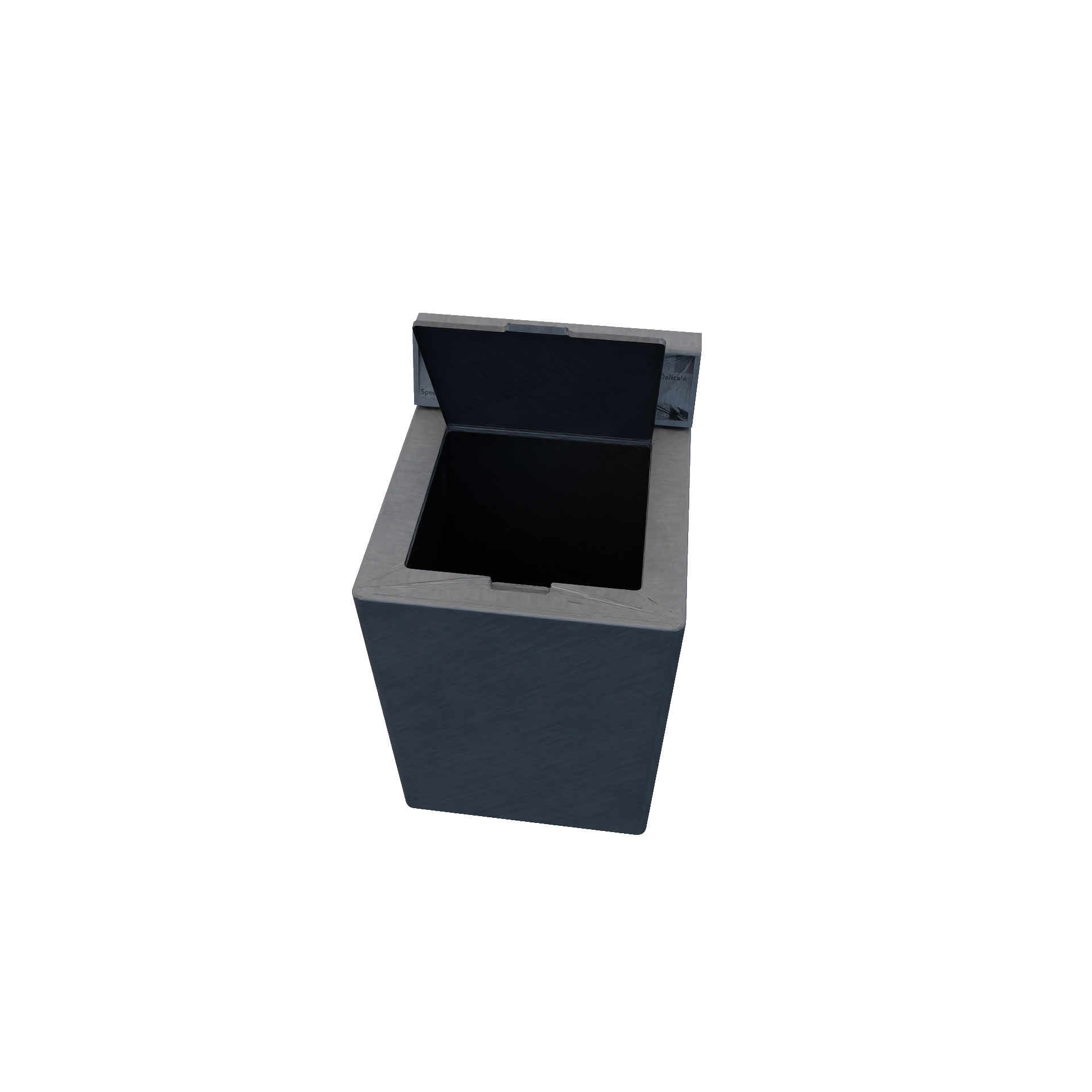
WasherRuleEncapsulates washing mechanism (e.g.: cleaning clothes in the washing machine with detergent). Washing behavior (i.e.: what types of particles are removed from clothes during washing) is predefined. Required Candidates
Conditions
Transition
|
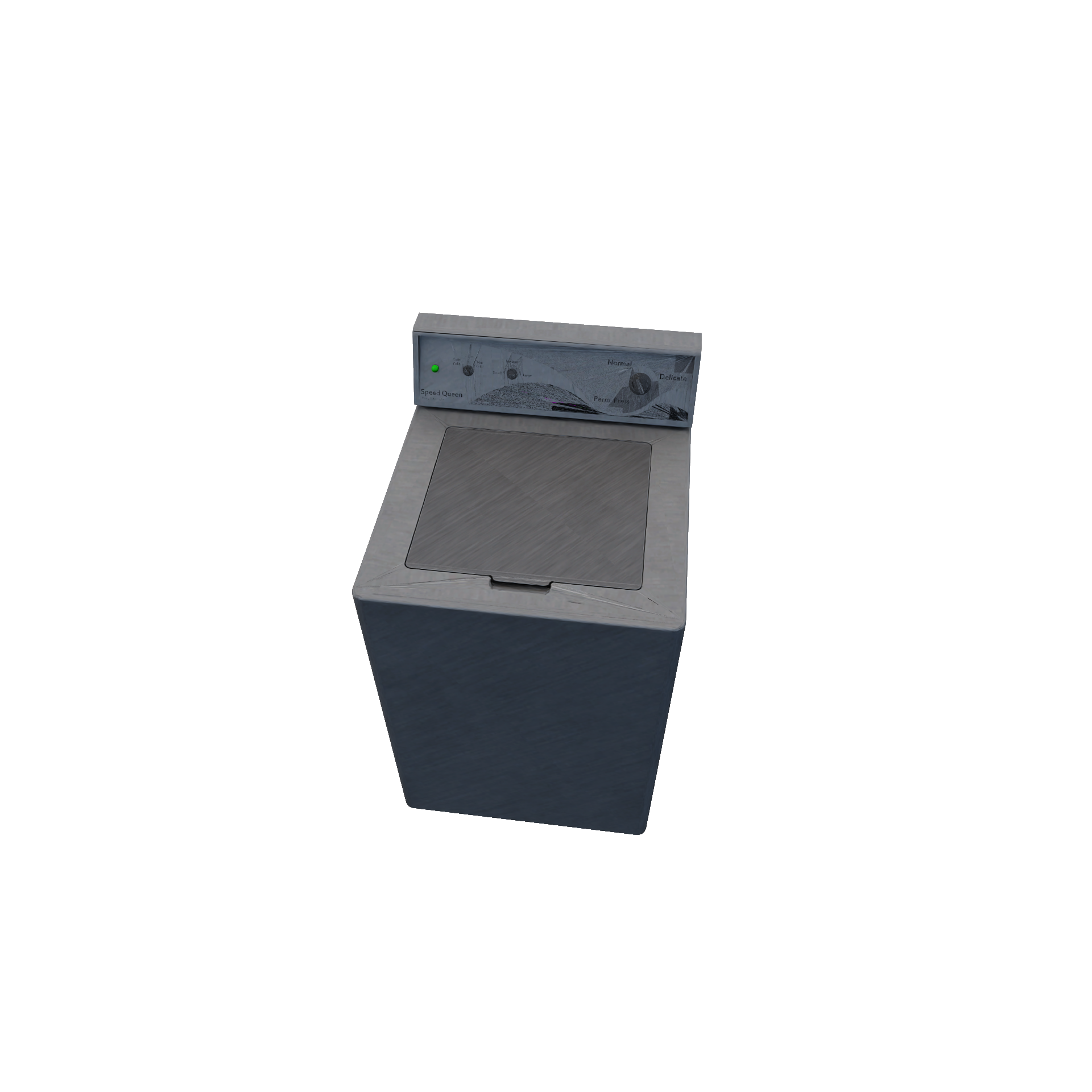

|
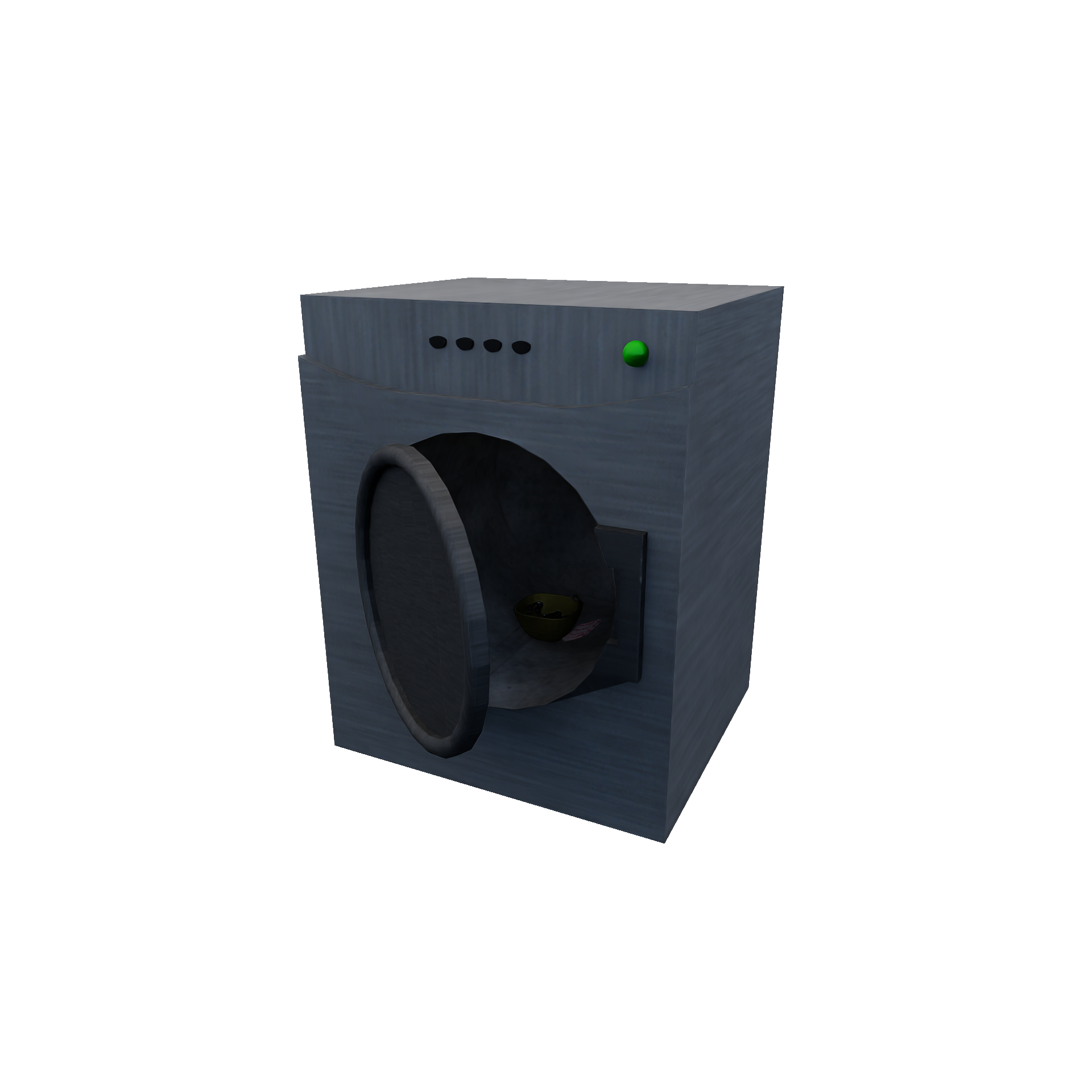
DryerRuleEncapsulates drying mechanism (e.g.: drying clothes in the drying machine). Required Candidates
Conditions
Transition
|
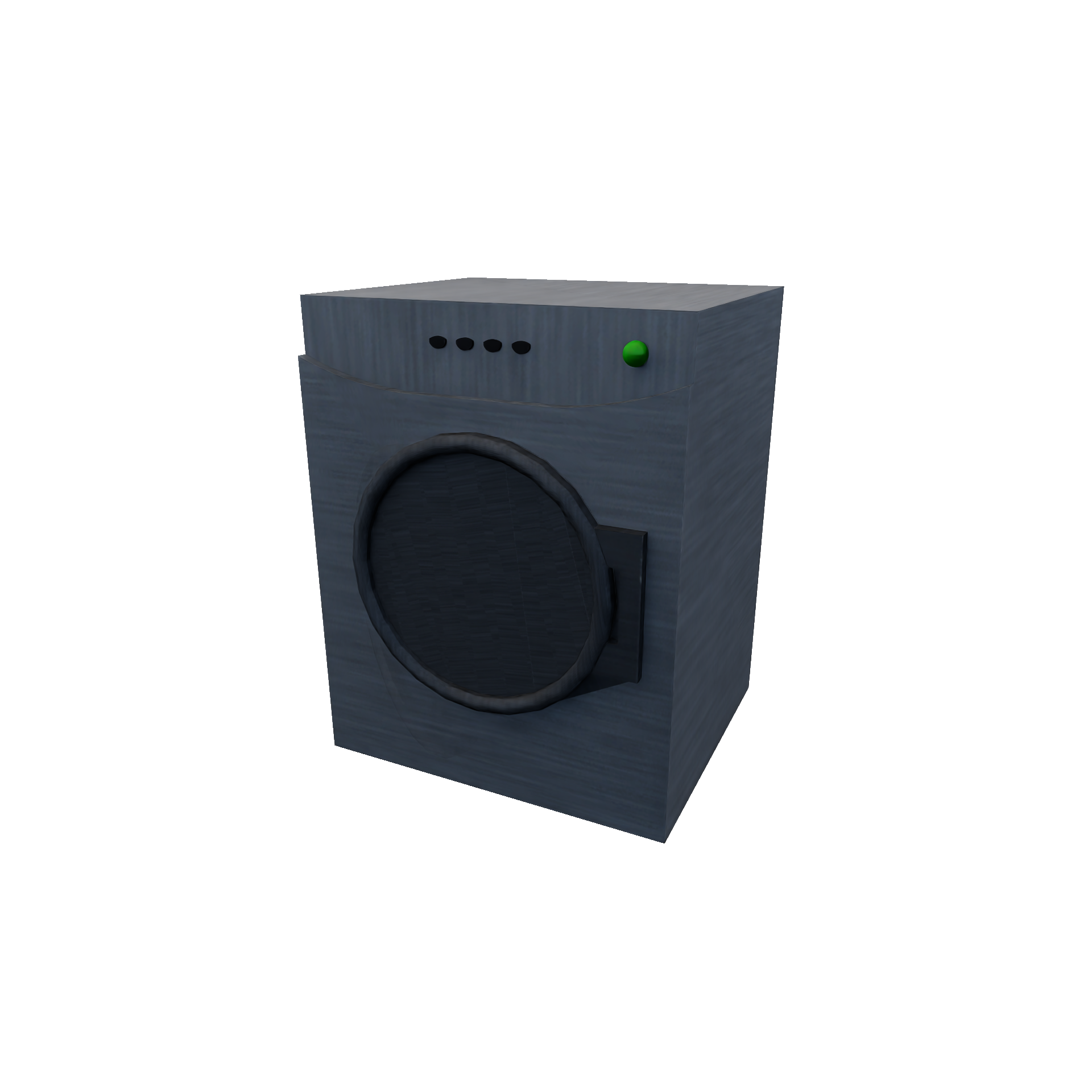

|